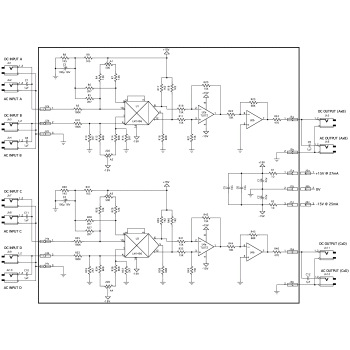
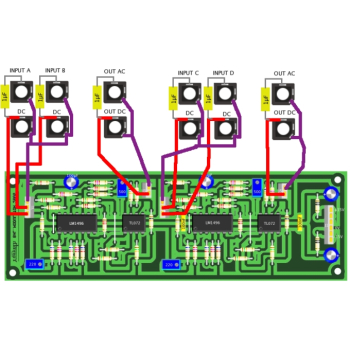
These resistors are suitable for use in both hobby projects se as well as commercial / industrial equipment. Supplied in packs of 100. Resistor value as per product title.
| Power rating | 0.25W @ 70°C | |
| Resistance range | 1Ω to 1MΩ | |
| Tolerance | ±1% | |
| Max. working voltage | 300V | |
| Max. overload voltage | 600V | |
| Max. temperature coefficient | 50ppm/°C | |
| Typical noise | 0.01µV/V | |
| Temperature range | –25°C to +70°C | |
| Dimensions | Body | 6.3 x 2.3mm dia. |
| Leads | 28 x 0.6mm dia. |
Downloads