Introduction
We find that wiring a MFOS PCB to the front panel controls is both time consuming and often detracts from the overall finish. We are not able to alter the MFOS PCBs to make panel wiring easier so we approached the problem from a different angle. We chose to mount the front panel controls on a mini PCBs (breakout boards) that take the panel controls to a JST type XH socket into which is plugged a lead. This lead is then dressed to the main MFOS PCB (or sometimes to other panel controls) and soldered into the respective pads. Many breakout boards have solderable jumpers for making common connections as well as thin tracks to cut where panel mounted resistors need to be connected inline with say a pot wiper. MFOS projects may require multiple breakout boards so we bundle these altogether and offer them in one ST Synth Panel Breakout PCB Set. The pack description will further describe the wiring colour code and what if any links need to be made or cut.
This method does have other advantages other than just time saving and appearance:
- Time saving
- Neater more professional appearance - improves resale value
- Takes care of common connections between panel components
- Has space to accommodate panel mounted resistors and capacitors
- Can improve reliability - have you tried soldering a diode, LED and a wire to one pin on a toggle switch on the 16-step sequencer?
- Makes fault finding easier
If you have any reservations about using connectors, then simply solder wires direct to the breakout boards. Takes longer but you still get all of the other advantages.
The boards are designed to fit our front panel component spacing so you will see references to pitch and whether it is in the 'x' or 'y' or both direction. At the time of writing, there was 30+ breakout boards developed for pots (using pot brackets), sockets (jack and banana), switches and LEDs. Whilst these will not take care of every panel component on over 40 MFOS projects, it will go a long way to achieving it. As we work through making up each MFOS project with these breakout boards, we will see where improvements can be made or even create more breakout boards to provide the best possible solution.
Specific Information on the 4-Pot Panel PCB (32.5y Pitch). Board size: 129x24mm
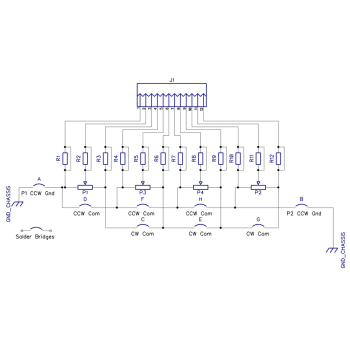
7210-704 accommodates 4 of our commercial grade synth pots along with our pot mounting brackets on a 32.5mm vertical pitch. Click the schematic image above to see the circuit for this board. Each of the pot terminals is wired through to a 12-way connector / lead (see 'Related Products' tab above. It is possible to include a resistor in any or all of the pot terminals (R1 to R12) although the thin track between the square pads on the underside will need to be cut where a resistor is used in that position. A resistor or resistors are rarely needed but when required, it is specifically mentioned in the ST Synth Panel Breakout PCB Set for the MFOS project.
8 solderable jumpers are provided and are labelled A to H:
- A - Connects the CCW terminal of pot 1 to ground
- B - Connects the CCW terminal of pot 2 to ground
- C- Connects the CW terminals of pot 1 to pot 3
- D- Connects the CCW terminals of pot 1 to pot 3
- E - Connects the CW terminals of pot 3 to pot 4
- F - Connects the CCW terminals of pot 3 to pot 4
- G - Connects the CW terminals of pot 4 to pot 2
- H - Connects the CCW terminals of pot 4 to pot 2
Note: Pots are numbered 1-3-4-2 on the current batch of PCBs
Two ground connection pads are provided for connecting the board to 0V (ground).
It is quite common in MFOS projects to have the CCW (counter-clockwise or anti-clockwise) terminals on the pots linked together and to ground. So in this case by way of example, you would solder across jumpers A, B, D, F & H. You would then connect one of the ground pads to your ground connection which could be on the main MFOS PCB or to another breakout board. Some breakout boards also have the ground connection wired to the JST socket which would make that board the preference for being the end of line ground connection back to the MFOS board.
Assembly
- First cut any tracks for resistors if required
- Solder across any jumpers as required
- Solder in the socket noting that the slots in the socket housing point towards the top of the board
- Remove any anti-rotation lugs on the pots
- Insert pot into bracket and temporarily do up lock nut
- Insert pot with bracket into PCB and solder in position ensuring the pot bracket sits flat on PCB. Only solder the bracket lugs on the bottom of the board - see below for why)
- Repeat for remaining pots
- Remove pot nuts
- Install assembled board into panel front and tighten pot nuts (washers not required)
- Plug in cable assembly and wire to main MFOS PCB as required

Wiring Colour Code
We actually managed to get the connector orientation wrong for the PCB layout. However, as long as you only solder the pot bracket lugs on the bottom of the PCB there is still plenty of room for the connector. Pin 1 (black wire) is on the left hand side of the board next to R6.
| Colour | Function |
| Black | Pot 1 CCW |
| Red | Pot 1 Slider |
| White | Pot 1 CW |
| Yellow | Pot 3 CCW |
| Orange | Pot 3 Slider |
| Green | Pot 3 CW |
| Blue | Pot 4 CCW |
| Violet | Pot 4 Slider |
| Grey | Pot 4 CW |
| Brown | Pot 2 CCW |
| Black | Pot 2 Slider |
| Red | Pot 2 CW |
It is always worth checking the wire colour sequence to ensure it matches the above just in case there has been a mistake at the factory in the assembly of the cable.
Typical examples of projects that use this board: VCF VC SVF, Quad Timbre Bank, ADSR, Dual AR, Delayed Modulator, Micro S&H, VC S&H, Sub-Commander, Multi Function, Stereo Auto Panner, Stereo Panning Mixer, Noise Generator, Phase Shifter, Ring Modulator, Wave Freaker, VC Echo, Noise Toaster, Sound Labs, Synth DIY Experimenter.